what is a deferred tax provision
Deferred tax refers to the tax effect of temporary differences between accounting income that is calculated as per provisions of Companies Act 2013 and taxable income that is calculated as per provisions of Income Tax Act 1961. Calculating the provision for income taxes under ASC 740 presents a difficult technical challenge.

Worked Example Accounting For Deferred Tax Assets The Footnotes Analyst
Lets look at an example.
. Items in financial statement that may be used to reduce taxable income in the future are called deferred tax assets. Depending upon nature of temporary differences following two types of deferred tax provision can be recognized. A deferred tax asset is an asset to the Company that usually arises when either the Company has overpaid taxes or paid advance tax.
Generally FRS 102 adopts a timing difference approach ie deferred tax is recognised when items of income and expenditure are. ASC 740 Provision for Income Taxes. ASC 740 governs how companies recognize the effects of income taxes on their financial statements under US.
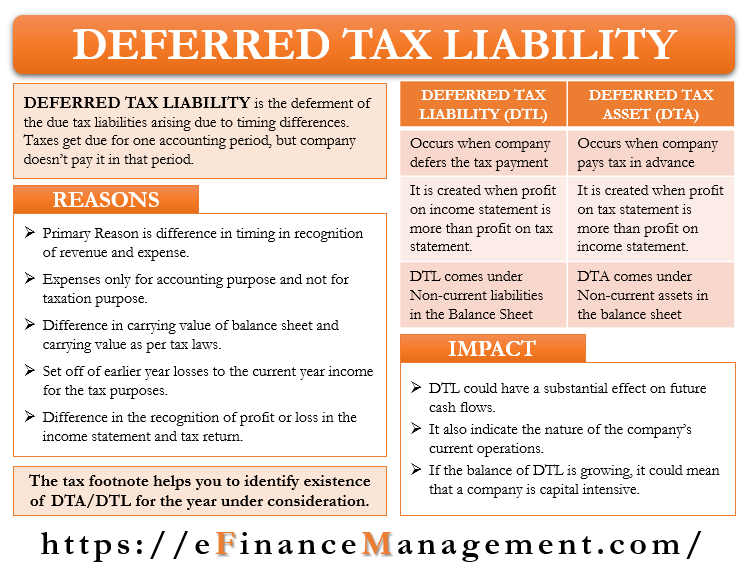
As the taxable temporary differences give rise to deferred tax liabilities those are all negative amounts. As per this definition there are two types of deferred tax-deferred tax asset and deferred tax liability. The balance on the deferred tax liability account is 150 representing the future liability of the business to pay tax on the income for the period.
Deferred tax liabilities can arise as a result of corporate taxation treatment of capital expenditure being more rapid than the accounting depreciation treatment. Deferred income tax is a balance sheet item which can either be a liability or an asset as it is a difference resulting from recognition of income between the accounting records of the company and the tax law because of which the income tax payable by the company is not equal to the total expense of tax reported. Deferred income tax expense.
A business has profits each year of 5000 before any depreciation charge. IAS 12 defines a deferred tax liability as being the amount of income tax payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences. In ABCs case it relates only to machinery.
Deferred tax is the amount of tax payable or recoverable in future reporting periods as a result of transactions or events recognised in current or previous periods accounts. The effect of accounting for the deferred tax liability is to apply the matching principle to the financial. In the last column of the table ABC can calculate its deferred tax asset or liability.
The term deferred tax in essence refers to the tax which shall either be paid or has already been settled due to transient inconsistency between an organisations income statement and tax statement. This more complicated part of the income tax provision calculates a cumulative total of the temporary differences and applies the appropriate tax rate to that total. However to understand this definition more fully it is necessary to explain the term taxable temporary differences.
Temporary differences Definition of temporary differences. Keep track of your business tax with instant financial reports at your fingertips with Debitoor accounting invoicing software. This article Deferred tax provisions 123 kb sets out four key areas of your tax provision that could be affected by the impacts of COVID-19.
Such taxes are recorded as an asset on the balance sheet and are eventually paid back to the Company or deducted from future taxes. Deferred income tax and current income tax comprise total tax expense in the income statement. So in simple terms deferred tax is tax that is payable in the future.
Timing differences are the differences between taxable income and accounting income for a period that originate in one period and are capable of reversal in one or more subsequent periods. Deferred tax is the tax effect that occurs due to the temporary differences either taxable temporary difference or deductible temporary difference. A provision is created when deferred tax is charged to the profit and loss account and this provision is reduced as the timing difference reduces.
Deferred tax is the tax effect of timing differences. This applies only to taxes based on incomenot sales payroll or property taxesper ASC 740-10. Deferred tax is a notional asset or liability to reflect corporate income taxation on a basis that is the same or more similar to recognition of profits than the taxation treatment.
Deferred tax can fall into one of two categories. Deferred income tax is recognised under IAS 12 to account for differences between tax base of an asset or a liability and its carrying amount. A deferred tax often represents the mathematical difference between the book carrying value ie an amount recorded in the accounting balance sheet for an asset or liability and a corresponding tax basis determined under the tax laws of that jurisdiction in the asset or liability multiplied by the applicable jurisdictions statutory income.
Deferred tax is a topic that is consistently tested in Paper F7 Financial Reporting and is often tested in further detail in Paper P2 Corporate Reporting. The income tax payable account has a balance of 1850 representing the current tax payable to the tax authorities. This article will start by considering aspects of deferred tax that are relevant to Paper F7 before moving on to the more complicated situations that may be tested in Paper P2.
The deferred income tax is a liability that the company has on its balance sheet but that is not due for payment yet. Deferred tax refers to either a positive asset or negative liability entry on a companys balance sheet regarding tax owed or overpaid due to temporary differences. Around the world governments are stepping in to try and limit the impact of the pandemic by providing financial support in numerous ways from direct cash payments through to the deferral of tax payments.
Deferred income tax is a result of the difference in income recognition between tax laws ie the IRS and accounting methods ie GAAP. Try it free for 7 days. Deferred tax asset liability is booked in accounts to neutralize those temporarytiming differences arising due to accounting policies followed by the business and the treatments allowed under tax laws.
The company usually either has deferred tax liability or deferred tax asset as the deferred tax would be net off between deferred tax liability and deferred asset. Calculate deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability.
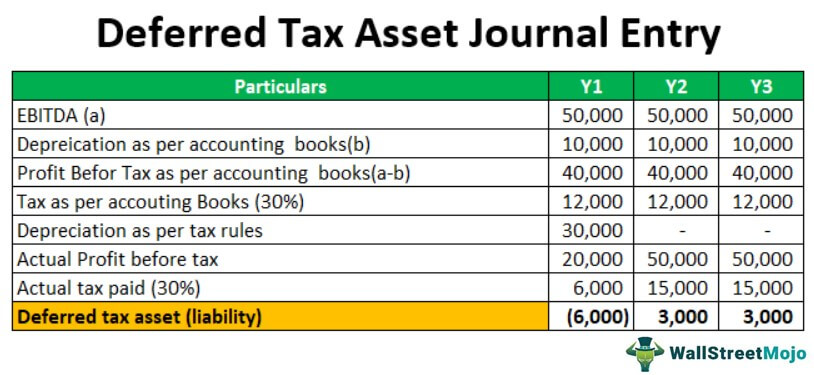
Deferred Tax Asset Journal Entry How To Recognize
Define Deferred Tax Liability Or Asset Accounting Clarified

Net Operating Losses Deferred Tax Assets Tutorial

Deferred Tax Double Entry Bookkeeping
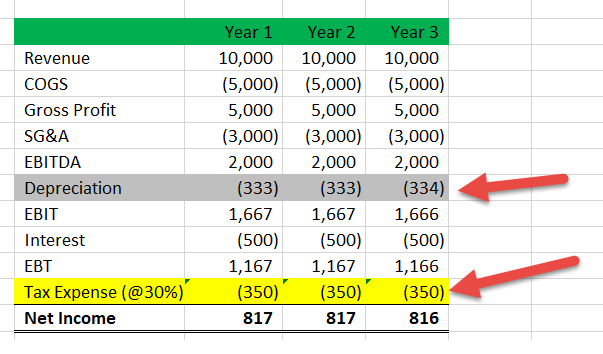
Deferred Tax Liabilities Meaning Example How To Calculate
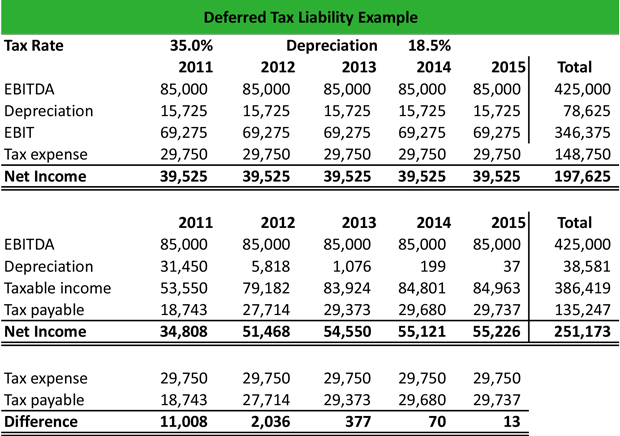
What Is A Deferred Tax Liability Dtl Definition Meaning Example

Deferred Tax Asset Journal Entry How To Recognize
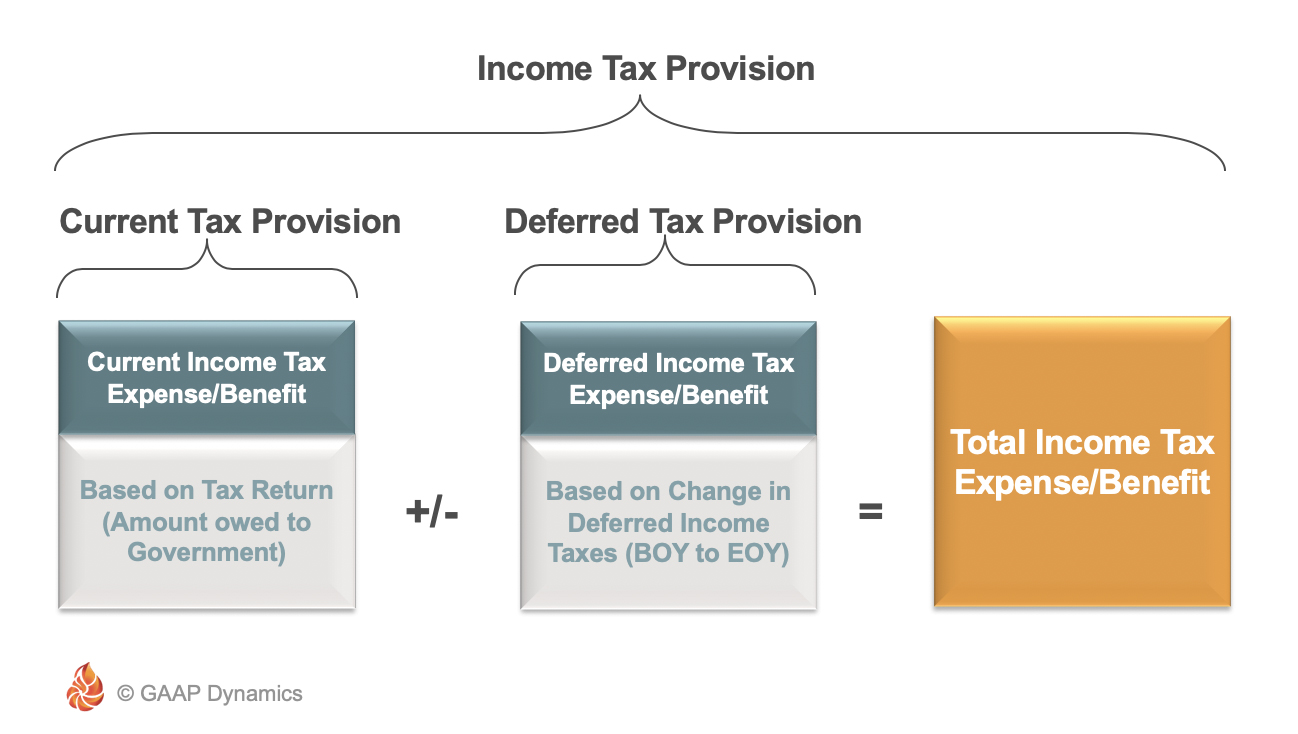
Accounting For Income Taxes Under Asc 740 Deferred Taxes Gaap Dynamics
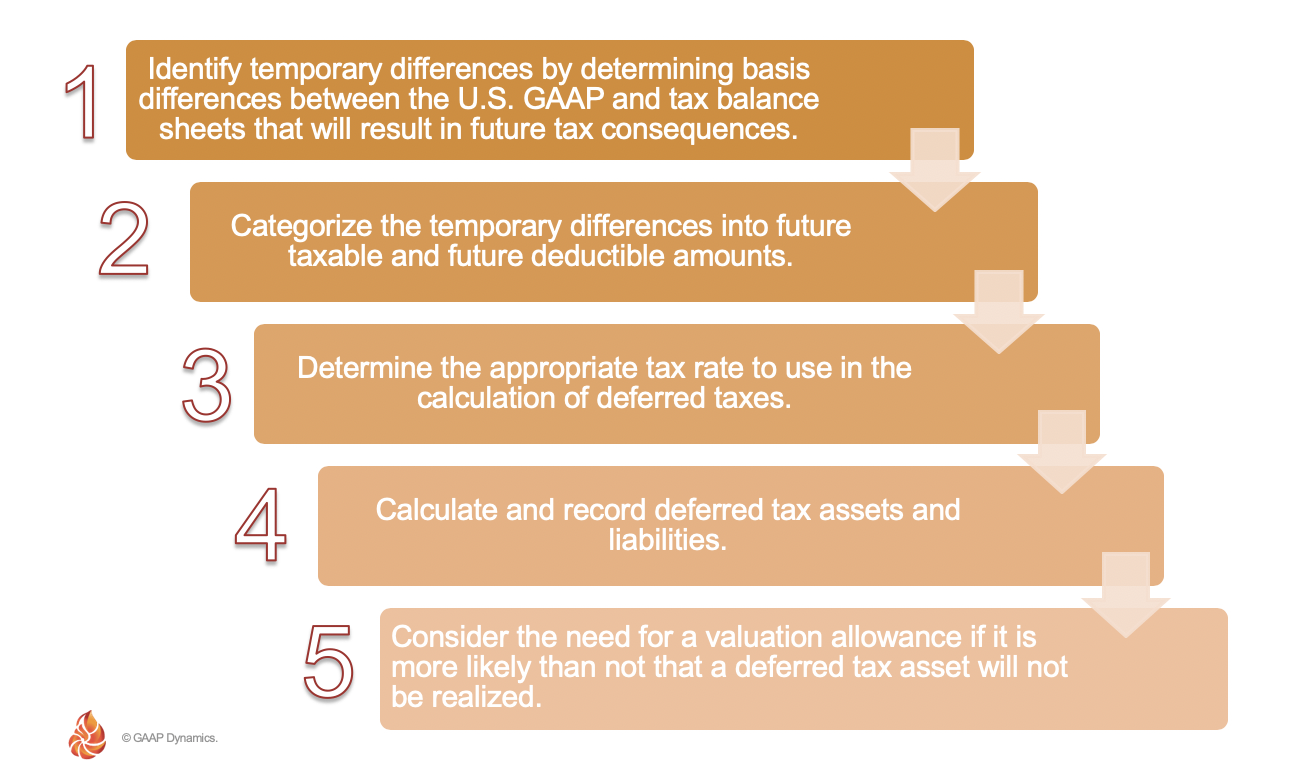
Accounting For Income Taxes Under Asc 740 Deferred Taxes Gaap Dynamics

Deferred Tax Meaning Expense Examples Calculation
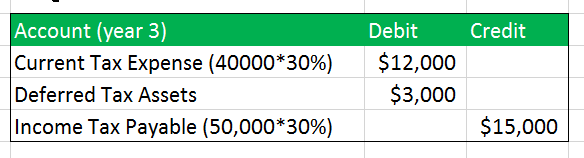
Deferred Tax Asset Journal Entry How To Recognize
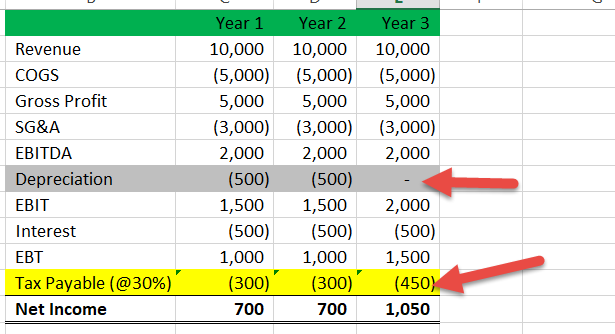
Deferred Tax Liabilities Meaning Example How To Calculate

/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)


/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)